Even though search engines are complex and technologically advanced systems, they are by no means perfect, and often, are not as effective as we'd all like them to be. For instance, search engines can sometimes struggle to interpret website data. To help search engines better understand the information on our webpage, we can 'mark-up' our webpages with something called 'schema markup', which makes page data easier for search engines to read and interpret.
Although schema markup has been around for a while, and is a very a powerful form of optimisation, very few sites actually use it and are missing out on potential benefits. In some cases, this is simply down to lack of knowledge, so with this article we hope to help our readers understand schema markup, and how to best use it.
What is Schema Markup?
Implementing Schema markup is the process of adding structured data elements to the code in your webpages. These structured elements make it easy for search engines to quickly, and easily read your web page, so that they can interpret your data and represent it in the correct way for appropriate searches. As a result of this structure, the search engines can very quickly pick out elements from your pages to show in the appropriate search result formats e.g. images, price lists, reviews, etc.
For example, let's assume you're writing an article about Philadelphia - the film that allowed Tom Hanks to pick up his first academy awards - you can mark it up using the 'movie' item type to inform the search engine that your page is about a film, and not the city, or the brand of cheese, and that way it will be picked up by the search engines and potentially displayed as part of their search results.
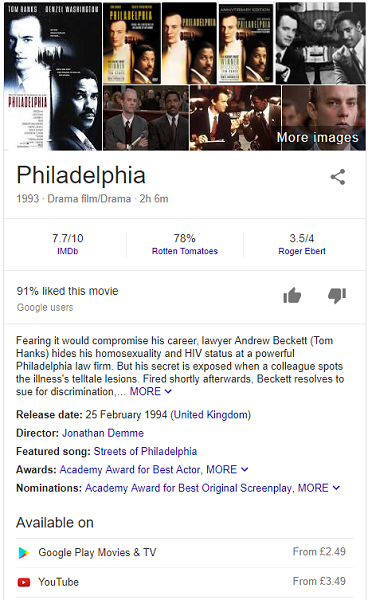
So, as you can see from the above snippet, Google have output a result that represents the film, gathering their images, links, dates, etc. from a variety of sources online. If you use schema markup correctly then they would potentially use your site as a source, and provide a link to it for the user to follow.
If your webpage isn't marked up in this way, it can still be read by the search engines of course, but essentially the easier and faster you make this for the likes of Google, the more likely your site will be shown in results like this. So, adding structured data allows you to provide clear context to your information.
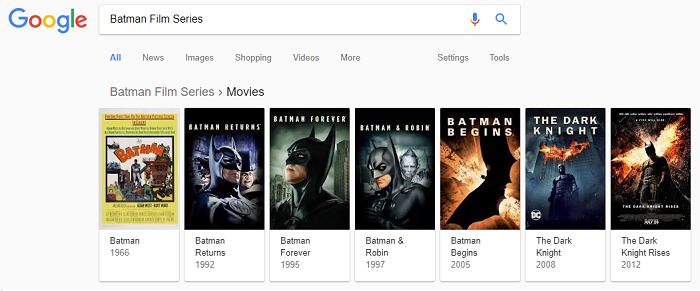
Another example of the use of structured data can be seen below, and in this instance the searcher has entered a term that Google have interpreted as - this person wants to see a film reel type result of batman films by date. This type of result displays a chronological order of the Batman films based on the search term 'Batman Film Series'.
There are in fact many different structures or layouts in the search engine results these days, and they all essentially come for schema markup from within appropriate websites. For example you've probably seen location-based results, image or product based results, event driven results, news feeds, etc.
Deciding what structured data to use can be difficult, and you may be worried that not every search engine will be able to understand your structured data markup - but there's no need to be concerned because this structured data has a standard which is controlled by Schema.org. In fact, if you want to learn more about schema you can visit their website, which is a great place to start when your planning your structured markup content.
Google, Bing, Yahoo!, and Yandex collaborated - yes, you read that correctly - to develop a specific vocabulary of tags (or microdata) that you can implement directly into your HTML, to help you define the different elements of your content - like reviews, opening times, dates of events, or images. This vocabulary helps to standardise schema markup and is fundamentally an agreed-upon set of code markers, or tags, that inform all the major search engines exactly what to do with your data.
How Does Schema Benefit SEO?
Schema markup helps to clearly define data elements in a page, often referred to as microdata, which in turn will make it easier for search engines to pull out the relevant parts of your webpage as and when they need it.
Search engines often refer to this microdata as Rich Data, Rich Cards or Rich Snippets, which essentially means that these bite size chunks allow them to produce richer results for their customer – the searcher.
So, by making it easier and faster for the search engines to index and retrieve your data, you in turn increase your chances of them choosing to show your website in search engine results, increasing your visibility and potentially your revenue.
We all use search engines to find products we want, and we all want faster results that are easier to decipher without having to click through lots of pages. So, this is what the search engines recognise, and schema markup allows them to get that data to the screen quicker, and present it in a smart way.
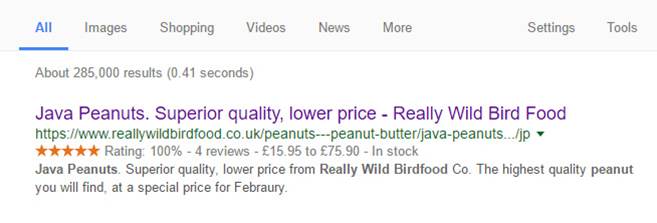
Take the below result for example, we don’t have to click on the page to see the price, the review rating, or whether they have stock of the Java Peanuts, it’s done simply in the search engine result itself with the aid of schema markup.
Here is an example of a website using schema markup
Now, schema by itself will not necessarily improve your rankings, but the more user friendly and search engine friendly you make your website, the more likely it is that you’ll appear high up in the search engine results. As discussed, schema markup will improve your visual offering and make it easier for the search engines to reach-in and pick out appropriate information; so really, it’s an obvious choice to include them.
Not only that; as we're in the age of artificial intelligence, and as voice search becomes more and more popular, the need to make your web pages easier for search engines to read is becoming increasingly more important.
Despite all this, only a small factor of the web uses schema markup on their websites - with schema.org claiming that only over 10 million websites have implemented schema markup, which is around 1% of the total number of websites in the world wide web.
So, what's stopping SEO's and website owners from implementing schema into their websites?
Why Aren't People Using Schema Markup?
If you're new to schema, or you struggle to understand code, marking up your webpage can be difficult, which is why most SEO's are put off by use this SEO technique. Even tools such as Google's Structured Data Markup Helper, which was designed to help you implement schema independently, requires you to have a good understanding of schema in order for you to use it to mark up your webpage.
Also, many SEO's struggle to understand schema markup vocabulary, and find that the information provided on the schema.org site hard to follow, and due to the lack of help and resources, many just give up trying to implement schema to their webpage, missing out on all the benefits.
Many people are also put off by using schema markup, because they feel it provides zero benefit in terms of traffic, with some SEO's even suggesting that they lose traffic from featured snippets because the web searcher can find what they're searching for without having to click through to their site. In most cases, this isn't going to be strictly true; of course if you're result shows data like a higher price, zero reviews or no stock, compared to the next result showing the opposite, then yes you just shot yourself in the foot, but to the end user this was useful information, right? So like anything its a case of strategizing how you present your markup in the results.
Despite the misunderstandings of schema markup, it is a seriously beneficial and useful SEO technique, and is one that is relatively easy to utilise if you have the understanding, and coding ability to implement. Here at Designer Websites, we have a team of expert web developers and SEO specialists that can optimise your website using schema markup, among other techniques of course, so please get in touch if you'd like to discuss further.
To request a quote or for more information on our website optimisation services, please click here.